Repository Summary
| Description | Real-time lidar-inertial odometry and mapping framework for dynamic environments |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/uts-ri/2fast2lamaa.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2025-12-19 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| ffastllamaa | 0.0.0 |
README
2Fast-2Lamaa
This repository contains our open-source implementation of 2Fast-2Lamaaa, a lidar-inertial mapping and localisation framework for large-scale environments.

If you are looking to use the undistortion-related code from our IROS publication, or the first version of 2Fast-2Lamaa, please refer to the old branch.
Abstract
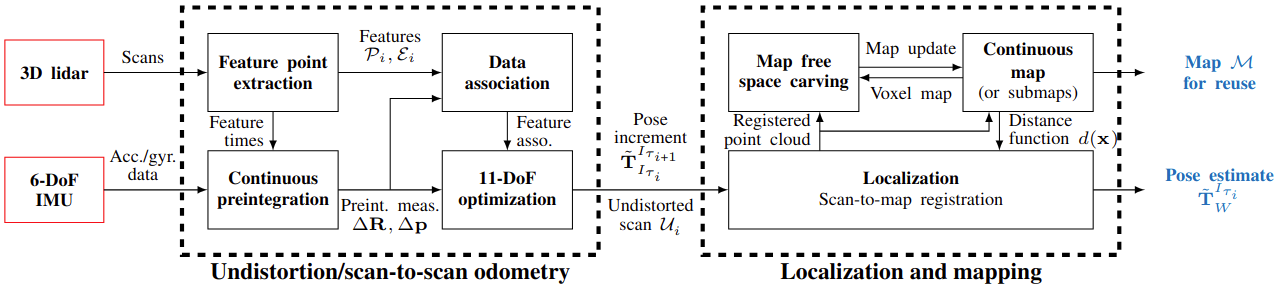
2Fast-2Lamaa stands for Fast Field-based Agent-Subtracted Truly coupled Lidar Localisation And Mapping with Accelerometer and Angular-rate. In other words, it performs localisation and mapping with a lidar and an IMU (accelerometer and angular-rate) using a Gaussian-Process-based distance field, and allows for dynamic object removal online or offline (agent-subtracted). The first key component of the proposed approach is the optimization-based undistortion of the lidar scans that leverages continuous IMU preintegration to model the system’s pose at every lidar point timestamp. The continuous trajectory of the system over a span of 100-200ms is parameterized solely by the initial conditions at the beginning of the scan (linear velocity and gravity orientation) and the IMU biases. This represents only eleven state variables that are estimated by minimizing point-to-line and point-to-plane distances between lidar-extracted features without relying on previous estimates, resulting in a prior-less motion-distortion correction strategy. As the proposed undistortion strategy performs local state estimation, it directly provides scan-to-scan odometry estimates. To enforce geometric consistency over longer periods of time, the undistorted scans are used for scan-to-map registration. The proposed map representation relies on Gaussian Processes to provide a continuous distance field, thus allowing point-to-surface distance queries anywhere in space. The poses of the undistorted lidar scans are corrected by minimizing such distances in a non-linear least-squares optimization. For odometry and mapping, the map is built incrementally in real-time, whereas for pure localization, it reuses existing maps. The incremental map building also includes mechanisms to remove dynamic objects from the scene. We extensively benchmark 2Fast-2Lamaa using 250km (over 10h) of public and self-collected datasets from both automotive and handheld systems. 2Fast-2Lamaa displays state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of challenging scenarios, with odometry and localization errors down to 0.27% and 0.06m, respectively.
A thourough presentation and performance analysis of 2Fast-2Lamaa is available in our paper’s preprint.
Corresponding contributor: le.gentil.cedric@gmail.com
Disclaimer
This code is provided as it is. It is research code that is not necessarily optimized for maintainability. We open-sourced this work for the benefit of the robotics community and we are open to suggestions/collaborations to improve this pipeline.
Citing
If you are using this framework or part of it please cite our work as shown at the bottom of this page
Installation
Dependencies
The following dependencies are required to build the package:
- ROS2
- Ceres
- Eigen
Please refer to the ROS2 installation guide with Ubuntu 24.04 for the installation of ROS2. The other dependencies can be installed using the following command:
sudo apt install libceres-dev libeigen3-dev
(if the default Ceres version is too old, you need to install Ceres 2.2 from source)
Building
To build the package, clone the repository in your ROS2 workspace and build it using colcon (if you don’t have a workspace yet, create ~/ros2_ws/src):
cd /path/to/your/workspace/src
git clone https://github.com/UTS-RI/2fast2lamaa.git
cd ..
colcon build --packages-select ffastllamaa
source install/setup.bash
Running
2Fast-2Lamaa is implemented as a ROS2 package named ffastllamaa.
Accordingly, you need your data to be in ROS2 bag format to run the package.
The lidar and IMU data should be pointcloud2 and imu messages, respectively.
You need to know the extrinsic calibration between the lidar and the IMU (the data should also be synchronised ideally)
Incorrect knowledge of the extrinsic calibration or bad synchronization will result in poor localisation and mapping performance.
As aforementioned, the core of 2Fast-2Lamaa is made of two main modules/nodes that are launched together via a launch file:
-
lidar_scan_odometry, the undistortion and dynamic object filtering node: it uses the IMU measurements to undistort the lidar scans in an optimization-based formulation -
gp_map, the localisation and mapping node: it uses the undistorted scans to perform localisation within a map (global or topometric) that can be built online of mapping, or provided for localisation only.
Thus, 2Fast-2Lamaa can be used in different modes: odometry/mapping or pure localisation. Both these modes can use a global map or a topometric map (set of submaps topologically linked). The mode and map style selection is done through node parameters (detailed below) that can be provided via the launch file.
Additionally, this repository also provides scripts/executables for:
- Offline dynamic object removal from 2Fast-2Lamaa-built maps
- Offline loop closure detection and pose graph optimisation
- Boreas dataset conversion towards ROS2 bags
Launching 2Fast-2Lamaa
Then you can run the package using the following command:
ros2 launch ffastllamaa <launch_file.launch.py>
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
