
|
linorobot2 repositoryrobotics ros robots autonomous gazebo diy amr ros2 4wd 2wd mecanum-wheel linorobot diy-robot |

|
linorobot2 repositoryrobotics ros robots autonomous gazebo diy amr ros2 4wd 2wd mecanum-wheel linorobot diy-robot |

|
linorobot2 repositoryrobotics ros robots autonomous gazebo diy amr ros2 4wd 2wd mecanum-wheel linorobot diy-robot |

|
linorobot2 repositoryrobotics ros robots autonomous gazebo diy amr ros2 4wd 2wd mecanum-wheel linorobot diy-robot |

|
linorobot2 repositoryrobotics ros robots autonomous gazebo diy amr ros2 4wd 2wd mecanum-wheel linorobot diy-robot linorobot2 linorobot2_base linorobot2_bringup linorobot2_description linorobot2_gazebo linorobot2_navigation |
Repository Summary
| Description | Autonomous mobile robots (2WD, 4WD, Mecanum Drive) |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/linorobot/linorobot2.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-02-09 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | robotics ros robots autonomous gazebo diy amr ros2 4wd 2wd mecanum-wheel linorobot diy-robot |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| linorobot2 | 0.0.0 |
| linorobot2_base | 0.0.0 |
| linorobot2_bringup | 0.0.0 |
| linorobot2_description | 0.0.0 |
| linorobot2_gazebo | 0.0.0 |
| linorobot2_navigation | 0.0.0 |
README
linorobot2
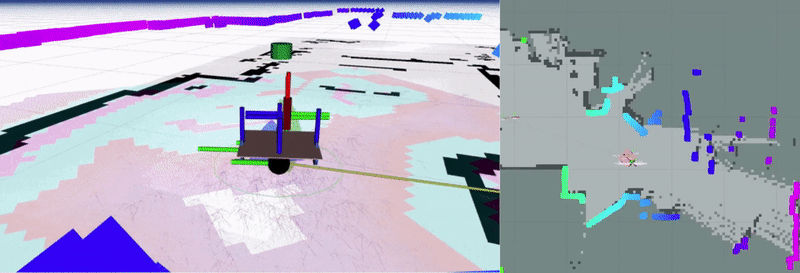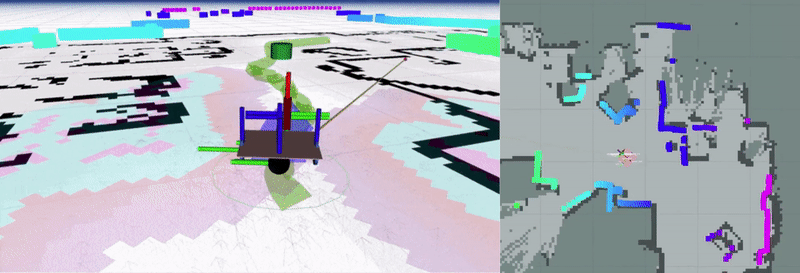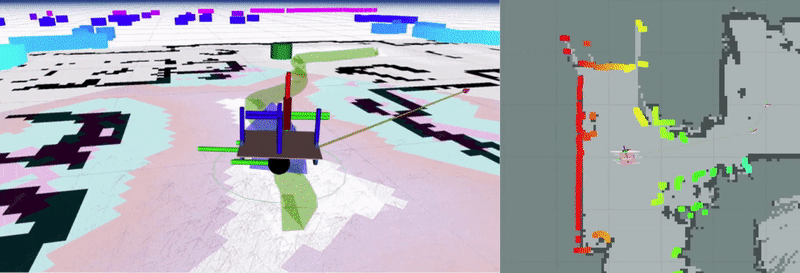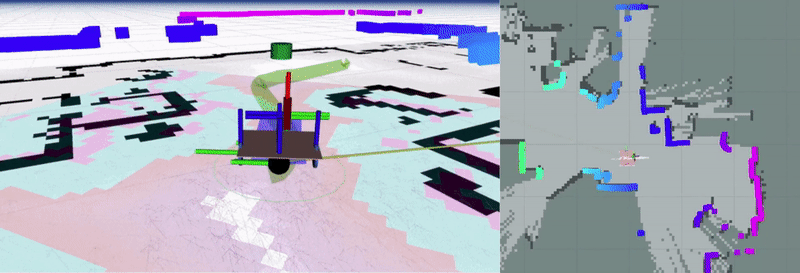
linorobot2 is a ROS2 implementation of the linorobot package for building custom robots with 2WD, 4WD, or Mecanum drive configurations. This package provides launch files for Nav2 integration and includes a complete simulation pipeline in Gazebo.
The software stack integrated in this package is hardware agnosticso users can switch between booting up the physical robot and spawning the virtual robot in Gazebo.
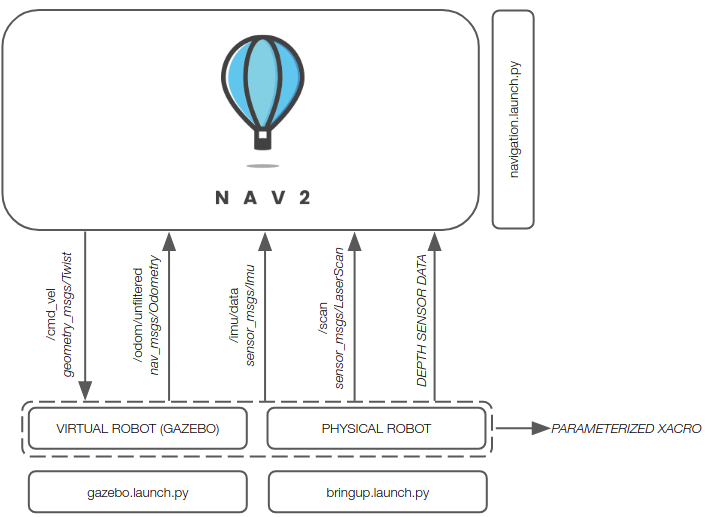
Assuming you’re using one of the tested sensors, linorobot2 automatically launches the necessary hardware drivers, with the topics being conveniently matched with the topics available in Gazebo. This allows users to define parameters for high level applications (ie. Nav2 SlamToolbox, AMCL) that are common to both virtual and physical robots.
The image below summarizes the topics available after running bringup.launch.py.
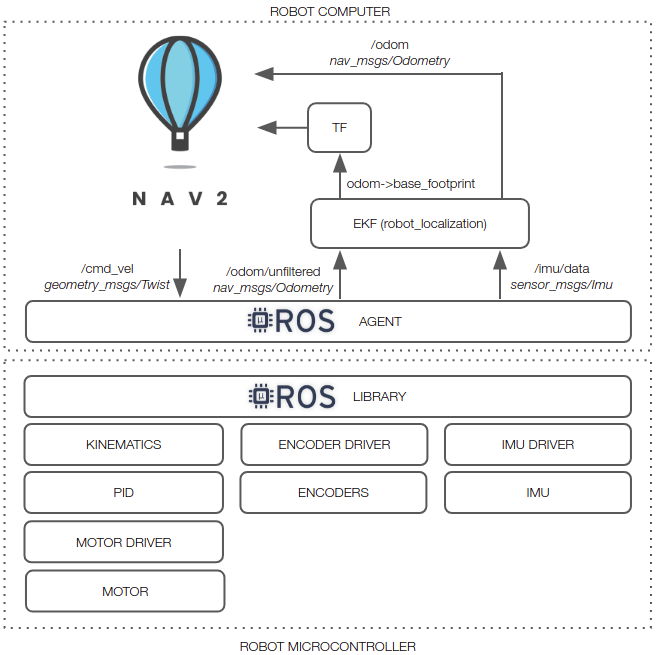
An in-depth tutorial on how to build the robot is available in linorobot2_hardware.
Installation
This package requires ros-foxy or ros-galactic. If you haven’t installed ROS2 yet, you can use this installer script that has been tested to work on x86 and ARM based dev boards ie. Raspberry Pi4/Nvidia Jetson Series.
1. Robot Computer - linorobot2 Package
The easiest way to install this package on the robot computer is to run the bash script found in this package’s root directory. It will install all the dependencies, set the ENV variables for the robot base and sensors, and create a linorobot2_ws (robot_computer_ws) on the robot computer’s $HOME directory. If you’re using a ZED camera with a Jetson Nano, you must create a custom Ubuntu 20.04 image for CUDA and the GPU driver to work. Here’s a quick guide on how to create a custom image for Jetson Nano.
source /opt/ros/<ros_distro>/setup.bash
cd /tmp
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/linorobot/linorobot2/${ROS_DISTRO}/install_linorobot2.bash
bash install_linorobot2.bash <robot_type> <laser_sensor> <depth_sensor>
source ~/.bashrc
robot_type:
-
2wd- 2 wheel drive robot. -
4wd- 4 wheel drive robot. -
mecanum- Mecanum drive robot.
laser_sensor:
-
a1- RPLIDAR A1 -
a2- RPLIDAR A2 -
a3- RPLIDAR A3 -
s1- RPLIDAR S1 -
s2- RPLIDAR S2 -
s3- RPLIDAR S3 -
c1- RPLIDAR A3 -
ld06- LD06 LIDAR -
ld19- LD19/LD300 LIDAR -
stl27l- STL27L LIDAR -
ydlidar- YDLIDAR -
xv11- XV11 -
realsense- * Intel RealSense D435, D435i -
zed- * Zed -
zed2- * Zed 2 -
zed2i- * Zed 2i -
zedm- * Zed Mini -
-- If the robot’s sensor is not listed above.
Sensors marked with an asterisk are depth sensors. If a depth sensor is used as a laser sensor, the launch files will run depthimage_to_laserscan to convert the depth sensor’s depth image to laser scans.
depth_sensor:
-
realsense- Intel RealSense D435, D435i -
zed- Zed -
zed2- Zed 2 -
zed2i- Zed 2i -
zedm- Zed Mini -
oakd- OAK D -
oakdlite- OAK D Lite -
oakdpro- OAK-D Pro
Alternatively, follow this guide to do the installation manually.
2. Host Machine / Development Computer - Gazebo Simulation (Optional)
This step is only required if you plan to use Gazebo later. This comes in handy if you want to fine-tune parameters (ie. SLAM Toolbox, AMCL, Nav2) or test your applications on a virtual robot.
2.1 Install linorobot2 Package
Install linorobot2 package on the host machine:
cd <host_machine_ws>
git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/linorobot/linorobot2 src/linorobot2
rosdep update && rosdep install --from-path src --ignore-src -y --skip-keys microxrcedds_agent --skip-keys micro_ros_agent
colcon build
source install/setup.bash
- microxrcedds_agent and micro_ros_agent dependency checks are skipped to prevent this issue of finding its keys. This means that you have to always add
--skip-keys microxrcedds_agent --skip-keys micro_ros_agentwhenever you have to runrosdep installon the ROS2 workspace where you installed linorobot2.
2.2 Define Robot Type
Set LINOROBOT2_BASE env variable to the type of robot base used. Available env variables are 2wd, 4wd, and mecanum. For example:
echo "export LINOROBOT2_BASE=2wd" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
You can skip the next step (Host Machine - RVIZ Configurations) since this package already contains the same RVIZ configurations to visualize the robot.
3. Host Machine - RVIZ Configurations
Install linorobot2_viz package to visualize the robot remotely specifically when creating a map or initializing/sending goal poses to the robot. The package has been separated to minimize the installation required if you’re not using the simulation tools on the host machine.
cd <host_machine_ws>
git clone https://github.com/linorobot/linorobot2_viz src/linorobot2_viz
rosdep update && rosdep install --from-path src --ignore-src -y
colcon build
source install/setup.bash
Hardware and Robot Firmware
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING

|
linorobot2 repositoryrobotics ros robots autonomous gazebo diy amr ros2 4wd 2wd mecanum-wheel linorobot diy-robot |

|
linorobot2 repositoryrobotics ros robots autonomous gazebo diy amr ros2 4wd 2wd mecanum-wheel linorobot diy-robot |

|
linorobot2 repositoryrobotics ros robots autonomous gazebo diy amr ros2 4wd 2wd mecanum-wheel linorobot diy-robot |

|
linorobot2 repositoryrobotics ros robots autonomous gazebo diy amr ros2 4wd 2wd mecanum-wheel linorobot diy-robot |