|
raspimouse_ros2_examples repositoryopencv raspberry-pi-mouse ros2 joystick-control raspimouse-ros2 raspimouse_ros2_examples |
|
|
Repository Summary
| Description | ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble-devel |
| Last Updated | 2024-08-28 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | opencv raspberry-pi-mouse ros2 joystick-control raspimouse-ros2 |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_ros2_examples | 2.2.1 |
README
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
Raspberry Pi MouseのROS 2サンプルコード集です。
ROS1のサンプルコード集はこちら。
Gazebo(シミュレータ)でも動作します。詳細はこちら。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
- Foxy
- Humble (This branch)
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 22.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
このリポジトリはApache 2.0ライセンスの元、公開されています。 ライセンスについてはLICENSEを参照ください。
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
ジョイスティックコントローラでRaspberryPiMouseを動かすコード例です。
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
デフォルトのキー割り当てはこちらです。
Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710を使う場合はモード切替スイッチを D (DirectInput Mode)に設定します。
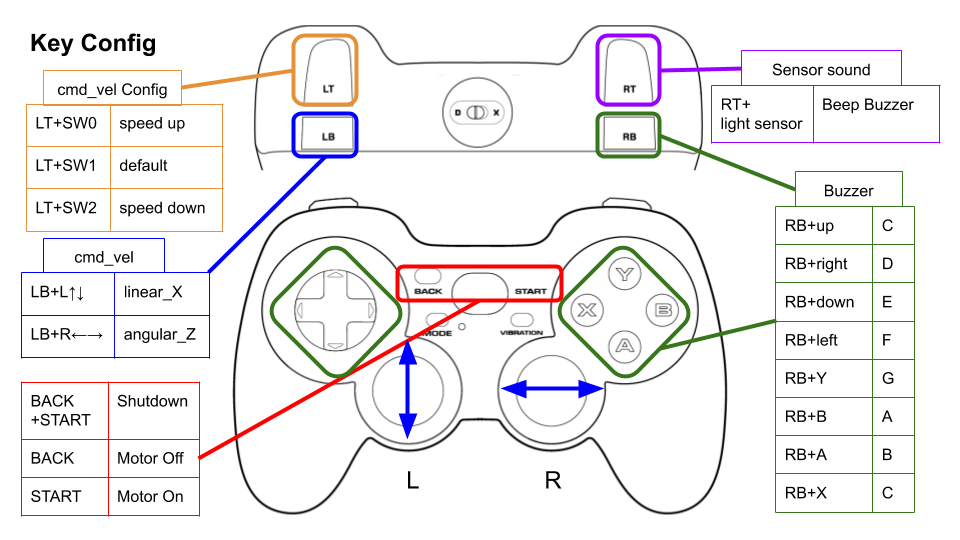
Configure
./config/joy_f710.yml、./config/joy_dualshock3.yml のキー番号を編集することで、キー割り当てを変更できます。
button_shutdown_1 : 8
button_shutdown_2 : 9
button_motor_off : 8
button_motor_on : 9
button_cmd_enable : 4
Videos
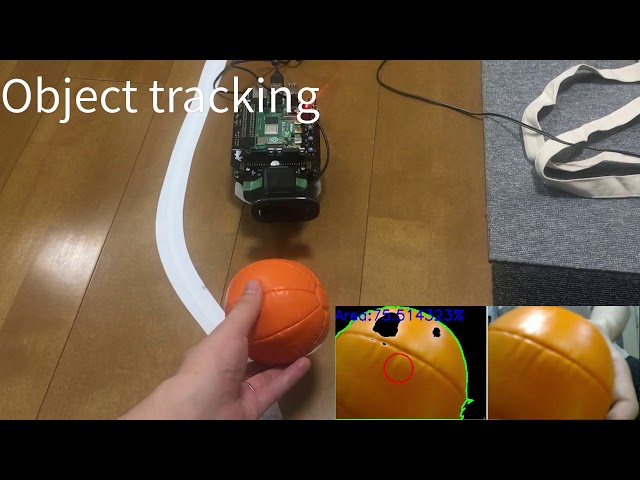
object_tracking
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/object_tracking.JPG width=500 />
色情報をもとにオレンジ色のボールの追跡を行うコード例です。 USB接続のWebカメラとOpenCVを使ってボール追跡をします。
Requirements
- Webカメラ
- カメラマウント
- ボール(Optional)
- Software
- OpenCV
- v4l-utils
Installation
Raspberry Pi Mouseにカメラマウントを取り付け、WebカメラをRaspberry Piに接続します。
How to use
次のスクリプトを実行して、カメラの自動調節機能(自動露光,オートホワイトバランス等)を切ります。
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src/raspimouse_ros2_examples/config
$ ./configure_camera.bash
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples object_tracking.launch.py video_device:=/dev/video0
カメラ画像はcamera/color/image_raw、物体検出画像はresult_imageというトピックとして発行されます。
これらの画像はRViz
やrqt_image_view
で表示できます。
画像を表示するとノードの動作が不安定になり、cmd_velや画像トピックが発行されないことがあります。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/object_tracking_ros2.png width=500 />
Configure
追跡対象の色を変更するには
./src/object_tracking_component.cpp
を編集します。
物体検出精度が悪い時にはカメラの露光や関数内のパラメータを調整して下さい。
void Tracker::tracking(const cv::Mat & input_frame, cv::Mat & result_frame)
{
cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(9, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(29, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Orange
// cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(60, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(80, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Green
// cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(100, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(120, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Blue
Videos
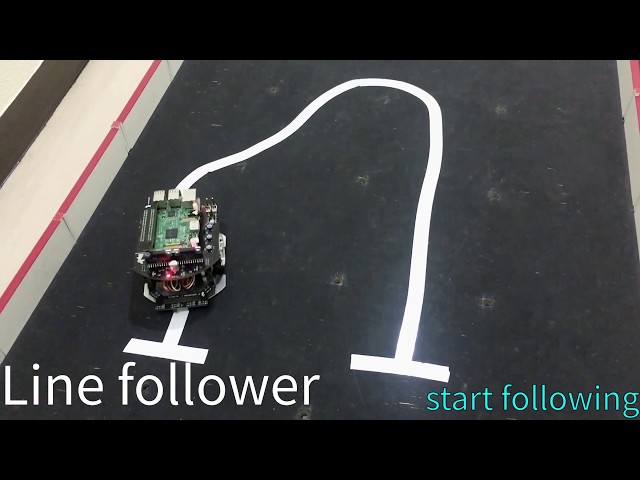
line_follower
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_with_line_trace_sensor.JPG width=500 />
ライントレースのコード例です。
Requirements
- ライントレースセンサ
- フィールドとライン (Optional)
Installation
Raspberry Pi Mouseにライントレースセンサを取り付けます。
How to use
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples line_follower.launch.py
Raspberry Pi Mouseをフィールドに置き、SW2を押してフィールド上のセンサ値をサンプリングします。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/field_calibration.JPG width=500 />
次に、センサとラインが重なるようにRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW1を押してライン上のセンサ値をサンプリングします。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/line_calibration.JPG width=500 />
最後に、ライン上にRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW0を押してライントレースを開始します。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/start_trace.JPG width=500 />
もう一度SW0を押すとライントレースを停止します。
Configure
走行速度を変更するには./src/line_follower_component.cppを編集します。
void Follower::publish_cmdvel_for_line_following(void)
{
const double VEL_LINEAR_X = 0.08; // m/s
const double VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.8; // rad/s
const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // rad/s
Videos
camera_line_follower
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_camera_line_trace_2.png width=500 />
RGBカメラによるライントレースのコード例です。
Requirements
Installation
Raspberry Pi Mouseにカメラマウントを取り付け、WebカメラをRaspberry Piに接続します。
How to use
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples camera_line_follower.launch.py video_device:=/dev/video0
ライン上にRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW2を押してライントレースを開始します。 停止させる場合はSW0を押します。
カメラ画像はcamera/color/image_raw、物体検出画像はresult_imageというトピックとして発行されます。
これらの画像はRViz
やrqt_image_view
で表示できます。
画像を表示するとノードの動作が不安定になり、cmd_velや画像トピックが発行されないことがあります。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/camera_line_trace.png width=500 />
Parameters
-
max_brightness- Type:
int - Default: 90
- 画像の2値化のしきい値の最大値
- Type:
-
min_brightness- Type:
int - Default: 0
- 画像の2値化のしきい値の最小値
- Type:
-
max_linear_vel- Type:
double - Default: 0.05
- 直進速度の最大値
- Type:
-
max_angular_vel- Type:
double - Default: 0.8
- 旋回速度の最大値
- Type:
-
area_threthold- Type:
double - Default: 0.20
- 走行を開始するためのライン面積のしきい値
- Type:
ros2 param set /camera_follower max_brightness 80
SLAM
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/slam_toolbox_ros2.png width=500 />
Raspberry Pi MouseでSLAMとNavigationを行うサンプルはrt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2へ移行しました。
direction_controller
<img src=https://www.rt-net.jp/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/img-usb9s_01.png width=500 />
IMUセンサを使用した角度制御のコード例です。
Requirements
- USB出力9軸IMUセンサモジュール
- LiDAR Mount (Raspberry Pi Mouse オプションキットNo.8 [マルチLiDARマウント])
- RT-USB-9axisIMU ROS Package
- https://github.com/rt-net/rt_usb_9axisimu_driver
Installation
LiDAR MountにIMUセンサモジュールを取り付けます。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_with_imu_2.JPG width=500 />
Raspberry Pi Mouse にLiDAR Mountを取り付けます。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_with_imu_1.JPG width=500 />
How to use
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples direction_controller.launch.py
SW0 ~ SW2を押して動作モードを切り替えます。
- SW0: ジャイロセンサのバイアスをキャリブレーションし、ラズパイマウスの方位角を
0 radにリセットします - SW1: 方位角を
0 radに維持する角度制御を開始します- SW0 ~ SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
- SW2: 方位角を
-π ~ π radに変化させる角度制御を開始します- SW0 ~ SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
Troubleshooting
IMUの接続が正常に行われない場合があります。
その時は、IMUのUSBケーブルを抜き差ししてください。
抜き差し実施後は、コマンドを再度実行してください。
Configure
パラメータで角度制御に使うPIDゲインを変更できます。
$ ros2 param set /direction_controller p_gain 10.0
Set parameter successful
$ ros2 param set /direction_controller i_gain 0.5
Set parameter successful
$ ros2 param set /direction_controller d_gain 0.0
Set parameter successful
Parameters
- p_gain
- Proportional gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- default: 10.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- type: double
- i_gain
- Integral gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- default: 0.0, min:0.0, max:5.0
- type: double
- d_gain
- Derivative gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- default: 20.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- type: double
- target_angle
- Target angle for the SW1 control mode.
- default: 0.0, min:-π, max:+π
- type: double
Publish topics
- heading_angle
- Heading angle of the robot that calculated from the IMU module sensor values.
- type: std_msgs/Float64
Videos
CONTRIBUTING
Any contribution that you make to this repository will be under the Apache 2 License, as dictated by that license:
5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
with Licensor regarding such Contributions.

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples repositoryopencv raspberry-pi-mouse ros2 joystick-control raspimouse-ros2 raspimouse_ros2_examples |
|
|
Repository Summary
| Description | ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | jazzy |
| Last Updated | 2024-11-25 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | opencv raspberry-pi-mouse ros2 joystick-control raspimouse-ros2 |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_ros2_examples | 3.0.0 |
README
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
Raspberry Pi MouseのROS 2サンプルコード集です。
ROS1のサンプルコード集はこちら。
Gazebo(シミュレータ)でも動作します。詳細はこちら。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Supported ROS 2 distributions
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 24.04
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
このリポジトリはApache 2.0ライセンスの元、公開されています。 ライセンスについてはLICENSEを参照ください。
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
ジョイスティックコントローラでRaspberryPiMouseを動かすコード例です。
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
デフォルトのキー割り当てはこちらです。
Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710を使う場合はモード切替スイッチを D (DirectInput Mode)に設定します。

Configure
./config/joy_f710.yml、./config/joy_dualshock3.yml のキー番号を編集することで、キー割り当てを変更できます。
button_shutdown_1 : 8
button_shutdown_2 : 9
button_motor_off : 8
button_motor_on : 9
button_cmd_enable : 4
Videos
object_tracking
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/object_tracking.JPG width=500 />
色情報をもとにオレンジ色のボールの追跡を行うコード例です。 USB接続のWebカメラとOpenCVを使ってボール追跡をします。
Requirements
- Webカメラ
- カメラマウント
- ボール(Optional)
- Software
- OpenCV
- v4l-utils
Installation
Raspberry Pi Mouseにカメラマウントを取り付け、WebカメラをRaspberry Piに接続します。
How to use
次のスクリプトを実行して、カメラの自動調節機能(自動露光,オートホワイトバランス等)を切ります。
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src/raspimouse_ros2_examples/config
$ ./configure_camera.bash
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples object_tracking.launch.py video_device:=/dev/video0
カメラ画像はcamera/color/image_raw、物体検出画像はresult_imageというトピックとして発行されます。
これらの画像はRViz
やrqt_image_view
で表示できます。
画像を表示するとノードの動作が不安定になり、cmd_velや画像トピックが発行されないことがあります。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/object_tracking_ros2.png width=500 />
Configure
追跡対象の色を変更するには
./src/object_tracking_component.cpp
を編集します。
物体検出精度が悪い時にはカメラの露光や関数内のパラメータを調整して下さい。
void Tracker::tracking(const cv::Mat & input_frame, cv::Mat & result_frame)
{
cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(9, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(29, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Orange
// cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(60, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(80, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Green
// cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(100, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(120, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Blue
Videos
line_follower
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_with_line_trace_sensor.JPG width=500 />
ライントレースのコード例です。
Requirements
- ライントレースセンサ
- フィールドとライン (Optional)
Installation
Raspberry Pi Mouseにライントレースセンサを取り付けます。
How to use
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples line_follower.launch.py
Raspberry Pi Mouseをフィールドに置き、SW2を押してフィールド上のセンサ値をサンプリングします。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/field_calibration.JPG width=500 />
次に、センサとラインが重なるようにRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW1を押してライン上のセンサ値をサンプリングします。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/line_calibration.JPG width=500 />
最後に、ライン上にRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW0を押してライントレースを開始します。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/start_trace.JPG width=500 />
もう一度SW0を押すとライントレースを停止します。
Configure
走行速度を変更するには./src/line_follower_component.cppを編集します。
void Follower::publish_cmdvel_for_line_following(void)
{
const double VEL_LINEAR_X = 0.08; // m/s
const double VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.8; // rad/s
const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // rad/s
Videos
camera_line_follower
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_camera_line_trace_2.png width=500 />
RGBカメラによるライントレースのコード例です。
Requirements
Installation
Raspberry Pi Mouseにカメラマウントを取り付け、WebカメラをRaspberry Piに接続します。
How to use
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples camera_line_follower.launch.py video_device:=/dev/video0
ライン上にRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW2を押してライントレースを開始します。 停止させる場合はSW0を押します。
カメラ画像はcamera/color/image_raw、物体検出画像はresult_imageというトピックとして発行されます。
これらの画像はRViz
やrqt_image_view
で表示できます。
画像を表示するとノードの動作が不安定になり、cmd_velや画像トピックが発行されないことがあります。
ラインの検出精度が悪い場合はカメラの露光やホワイトバランスの調整を行ってください。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/camera_line_trace.png width=500 />
Parameters
-
max_brightness- Type:
int - Default: 90
- 画像の2値化のしきい値の最大値
- Type:
-
min_brightness- Type:
int - Default: 0
- 画像の2値化のしきい値の最小値
- Type:
-
max_linear_vel- Type:
double - Default: 0.05
- 直進速度の最大値
- Type:
-
max_angular_vel- Type:
double - Default: 0.8
- 旋回速度の最大値
- Type:
-
area_threshold- Type:
double - Default: 0.20
- 走行を開始するためのライン面積のしきい値
- Type:
ros2 param set /camera_follower max_brightness 80
SLAM
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/slam_toolbox_ros2.png width=500 />
Raspberry Pi MouseでSLAMとNavigationを行うサンプルはrt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2へ移行しました。
direction_controller
<img src=https://www.rt-shop.jp/images/RT/RT-USB-9axisIMU.png width=200 /> <img src=https://www.rt-shop.jp/images/RT/%E8%A3%BD%E5%93%81%E5%86%99%E7%9C%9F.JPG height=200>
IMUセンサを使用した角度制御のコード例です。
Requirements
- USB出力9軸IMUセンサモジュール
- LiDAR Mount (Raspberry Pi Mouse オプションキットNo.8 [マルチLiDARマウント])
- RT-USB-9axisIMU ROS Package
- https://github.com/rt-net/rt_usb_9axisimu_driver
Installation
LiDAR MountにIMUセンサモジュールを取り付けます。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_with_imu_2.JPG width=500 />
Raspberry Pi Mouse にLiDAR Mountを取り付けます。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_with_imu_1.JPG width=500 />
How to use
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples direction_controller.launch.py
SW0 ~ SW2を押して動作モードを切り替えます。
- SW0: ジャイロセンサのバイアスをキャリブレーションし、ラズパイマウスの方位角を
0 radにリセットします - SW1: 方位角を
0 radに維持する角度制御を開始します- SW0 ~ SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
- SW2: 方位角を
-π ~ π radに変化させる角度制御を開始します- SW0 ~ SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
Troubleshooting
IMUの接続が正常に行われない場合があります。 その時は、IMUのUSBケーブルを抜き差ししてください。 抜き差し実施後は、コマンドを再度実行してください。
Configure
パラメータで角度制御に使うPIDゲインを変更できます。
$ ros2 param set /direction_controller p_gain 10.0
Set parameter successful
$ ros2 param set /direction_controller i_gain 0.5
Set parameter successful
$ ros2 param set /direction_controller d_gain 0.0
Set parameter successful
Parameters
- p_gain
- Proportional gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- default: 10.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- type: double
- i_gain
- Integral gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- default: 0.0, min:0.0, max:5.0
- type: double
- d_gain
- Derivative gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- default: 20.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- type: double
- target_angle
- Target angle for the SW1 control mode.
- default: 0.0, min:-π, max:+π
- type: double
Publish topics
- heading_angle
- Heading angle of the robot that calculated from the IMU module sensor values.
- type: std_msgs/Float64
Videos
CONTRIBUTING
Any contribution that you make to this repository will be under the Apache 2 License, as dictated by that license:
5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
with Licensor regarding such Contributions.

|
raspimouse_ros2_examples repositoryopencv raspberry-pi-mouse ros2 joystick-control raspimouse-ros2 raspimouse_ros2_examples |
|
|
Repository Summary
| Description | ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | foxy-devel |
| Last Updated | 2022-07-29 |
| Dev Status | MAINTAINED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | opencv raspberry-pi-mouse ros2 joystick-control raspimouse-ros2 |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| raspimouse_ros2_examples | 1.0.0 |
README
| English | 日本語 |
raspimouse_ros2_examples
Raspberry Pi MouseのROS 2サンプルコード集です。
ROS1のサンプルコード集はこちら。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/raspberry_pi_mouse.JPG width=500 />
Requirements
- Raspberry Pi Mouse
- https://rt-net.jp/products/raspberrypimousev3/
- Linux OS
- Ubuntu server 20.04
- https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi
- Device Driver
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- ROS
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
Installation
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
# Clone package
$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO-devel https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples
# Install dependencies
$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
# Build & Install
$ cd ~/ros2_ws
$ colcon build --symlink-install
$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
License
このリポジトリはApache 2.0ライセンスの元、公開されています。 ライセンスについてはLICENSEを参照ください。
How To Use Examples
joystick_control
ジョイスティックコントローラでRaspberryPiMouseを動かすコード例です。
Requirements
- Joystick Controller
How to use
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
# Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
## on RaspberryPiMouse
$ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
## on remote computer
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
デフォルトのキー割り当てはこちらです。
Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710を使う場合はモード切替スイッチを D (DirectInput Mode)に設定します。

Configure
./config/joy_f710.yml、./config/joy_dualshock3.yml のキー番号を編集することで、キー割り当てを変更できます。
button_shutdown_1 : 8
button_shutdown_2 : 9
button_motor_off : 8
button_motor_on : 9
button_cmd_enable : 4
Videos
object_tracking
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/object_tracking.JPG width=500 />
色情報をもとにオレンジ色のボールの追跡を行うコード例です。 USB接続のWebカメラとOpenCVを使ってボール追跡をします。
Requirements
- Webカメラ
- カメラマウント
- ボール(Optional)
- Software
- OpenCV
- v4l-utils
Installation
Raspberry Pi Mouseにカメラマウントを取り付け、WebカメラをRaspberry Piに接続します。
How to use
次のスクリプトを実行して、カメラの自動調節機能(自動露光,オートホワイトバランス等)を切ります。
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src/raspimouse_ros2_examples/config
$ ./configure_camera.bash
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples object_tracking.launch.py
カメラ画像はraw_image、物体検出画像はresult_imageというトピックとして発行されます。
これらの画像はRViz
やrqt_image_view
で表示できます。
画像を表示するとノードの動作が不安定になり、cmd_velや画像トピックが発行されないことがあります。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/object_tracking_ros2.png width=500 />
Configure
追跡対象の色を変更するには
./src/object_tracking_component.cpp
を編集します。
物体検出精度が悪い時にはカメラの露光や関数内のパラメータを調整して下さい。
void Tracker::tracking(const cv::Mat & input_frame, cv::Mat & result_frame)
{
cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(9, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(29, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Orange
// cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(60, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(80, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Green
// cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(100, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(120, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Blue
Videos
line_follower
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_with_line_trace_sensor.JPG width=500 />
ライントレースのコード例です。
Requirements
- ライントレースセンサ
- フィールドとライン (Optional)
Installation
Raspberry Pi Mouseにライントレースセンサを取り付けます。
How to use
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples line_follower.launch.py
Raspberry Pi Mouseをフィールドに置き、SW2を押してフィールド上のセンサ値をサンプリングします。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/field_calibration.JPG width=500 />
次に、センサとラインが重なるようにRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW1を押してライン上のセンサ値をサンプリングします。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/line_calibration.JPG width=500 />
最後に、ライン上にRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW0を押してライントレースを開始します。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/start_trace.JPG width=500 />
もう一度SW0を押すとライントレースを停止します。
Configure
走行速度を変更するには./src/line_follower_component.cppを編集します。
void Follower::publish_cmdvel_for_line_following(void)
{
const double VEL_LINEAR_X = 0.08; // m/s
const double VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.8; // rad/s
const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // rad/s
Videos
SLAM
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/slam_toolbox_ros2.png width=500 />
LiDARとslam_toolbox を使ってSLAM(自己位置推定と地図作成)を行うサンプルです。
Requirements
- LiDAR
<!– - ~URG-04LX-UG01~
- RPLIDAR A1 –>
- LDS-01
- LiDAR Mount
- Joystick Controller (Optional)
Installation
Raspberry Pi MouseにLiDARを取り付けます。
- LDS-01
- <img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_with_lds01.JPG width=500 />
How to use
Raspberry Pi Mouse上で次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
# LDS
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples mouse_with_lidar.launch.py lidar:=lds
Raspberry Pi Mouseを動かすためteleop_joy.launch.pyを起動します
# Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=false
次のコマンドでslam_toolboxパッケージを起動します。(Remote computerでの実行推奨)
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples slam.launch.py
Raspberry Pi Mouseを動かして地図を作成します。
次のコマンドで作成した地図を保存します。
$ mkdir ~/maps
$ ros2 run nav2_map_server map_saver_cli -f ~/maps/mymap --ros-args -p save_map_timeout:=10000
Configure SLAM parameters
./config/mapper_params_offline.yamlでslam_toolboxパッケージのパラメータを調節します。
Configure Odometry calculation
下記のようにmouse.ymlを編集し、use_pulse_countersをtrueに(初期値: false)することで、
raspimouseノードがモータの制御パルス数からオドメトリ(/odom)を計算します。
これは自己位置推定の精度を向上させます。
raspimouse:
ros__parameters:
odometry_scale_left_wheel : 1.0
odometry_scale_right_wheel: 1.0
use_light_sensors : true
use_pulse_counters : true
direction_controller
<img src=https://www.rt-net.jp/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/img-usb9s_01.png width=500 />
IMUセンサを使用した角度制御のコード例です。
Requirements
- USB出力9軸IMUセンサモジュール
- LiDAR Mount (Raspberry Pi Mouse オプションキットNo.8 [マルチLiDARマウント])
- RT-USB-9axisIMU ROS Package
- https://github.com/rt-net/rt_usb_9axisimu_driver
Installation
LiDAR MountにIMUセンサモジュールを取り付けます。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_with_imu_2.JPG width=500 />
Raspberry Pi Mouse にLiDAR Mountを取り付けます。
<img src=https://rt-net.github.io/images/raspberry-pi-mouse/mouse_with_imu_1.JPG width=500 />
How to use
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples direction_controller.launch.py
SW0 ~ SW2を押して動作モードを切り替えます。
- SW0: ジャイロセンサのバイアスをキャリブレーションし、ラズパイマウスの方位角を
0 radにリセットします - SW1: 方位角を
0 radに維持する角度制御を開始します- SW0 ~ SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
- SW2: 方位角を
-π ~ π radに変化させる角度制御を開始します- SW0 ~ SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
Configure
パラメータで角度制御に使うPIDゲインを変更できます。
$ ros2 param set /direction_controller p_gain 10.0
Set parameter successful
$ ros2 param set /direction_controller i_gain 0.5
Set parameter successful
$ ros2 param set /direction_controller d_gain 0.0
Set parameter successful
Parameters
- p_gain
- Proportional gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- default: 10.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- type: double
- i_gain
- Integral gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- default: 0.0, min:0.0, max:5.0
- type: double
- d_gain
- Derivative gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- default: 20.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- type: double
- target_angle
- Target angle for the SW1 control mode.
- default: 0.0, min:-π, max:+π
- type: double
Publish topics
- heading_angle
- Heading angle of the robot that calculated from the IMU module sensor values.
- type: std_msgs/Float64
Videos
CONTRIBUTING
Any contribution that you make to this repository will be under the Apache 2 License, as dictated by that license:
5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
with Licensor regarding such Contributions.