
|
ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot repositoryturtlebot3_drl turtlebot3_msgs turtlebot3_fake_node turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_simulations |
ROS Distro
|
Repository Summary
| Description | A ROS2-based framework for TurtleBot3-like DRL autonomous navigation |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/amjadmajid/ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2023-06-16 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| turtlebot3_drl | 2.0.0 |
| turtlebot3_msgs | 2.2.1 |
| turtlebot3_fake_node | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_gazebo | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_simulations | 2.2.3 |
README
This repository contains the code for a ROS2 implementation of several DRL algorithms for autonumous navigation with the Turtlebot3.
Authors:
- Tomas van Rietbergen
- Amjad Yousef Majid
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS

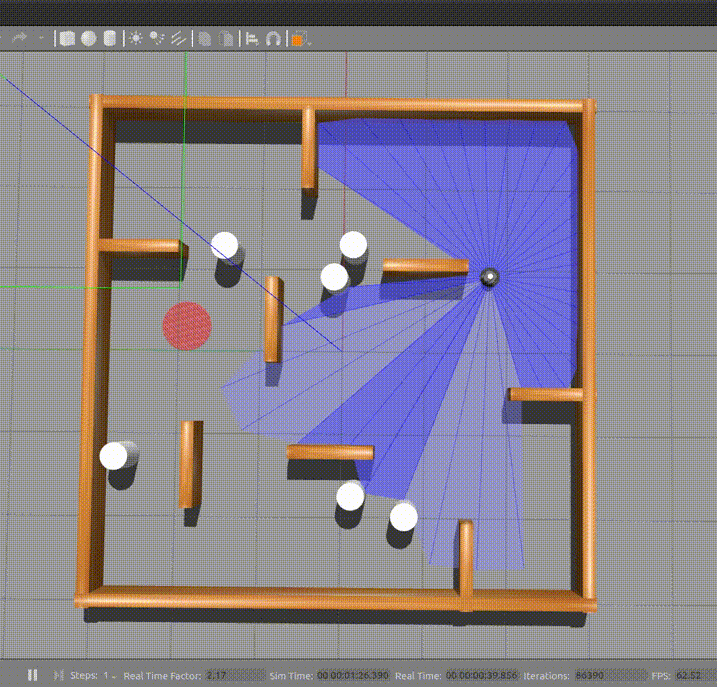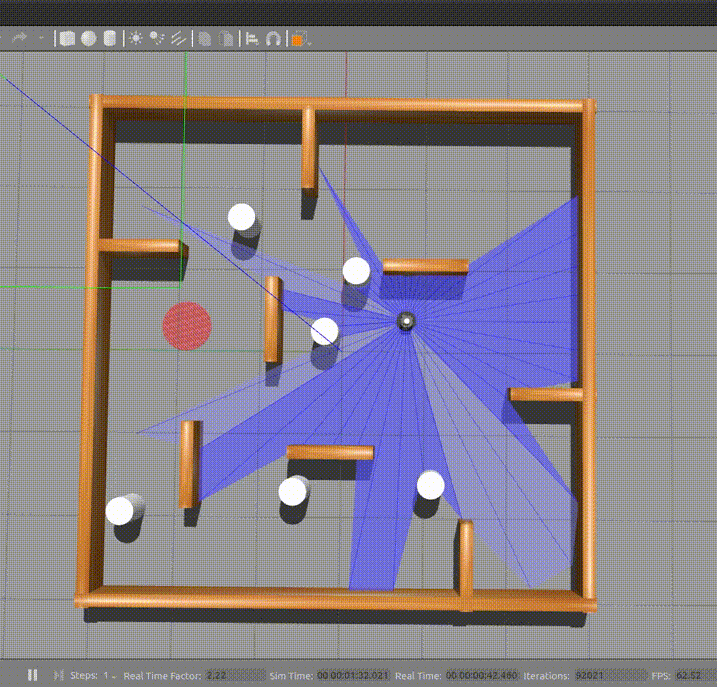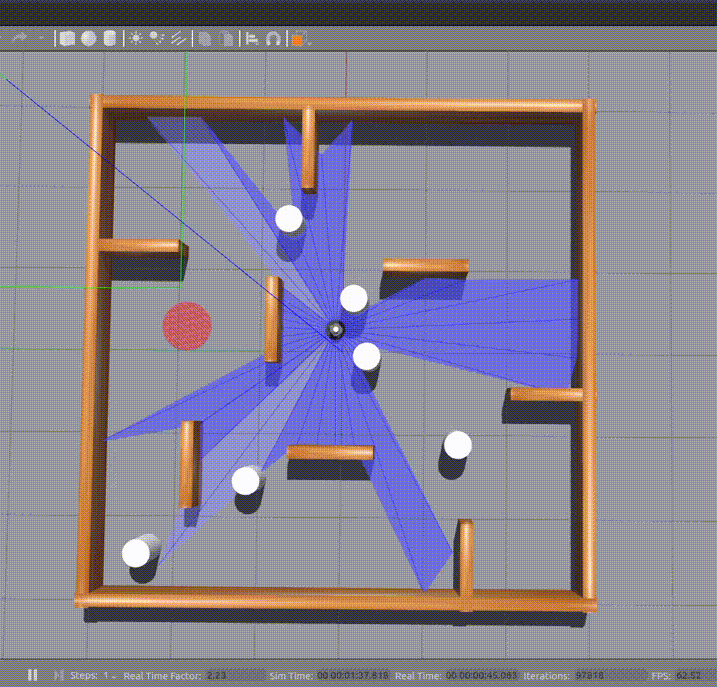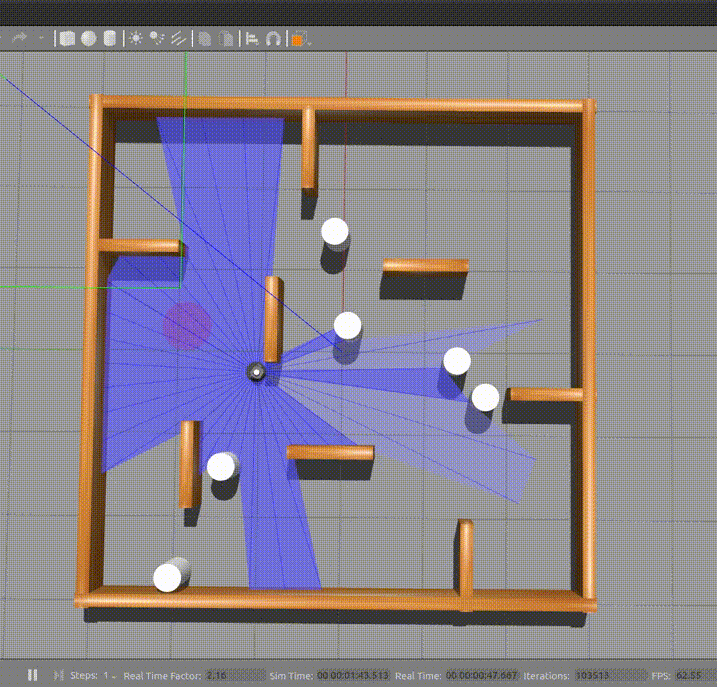


Dependencies
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa) download
- ROS2 Foxy Fitzroy download
- Gazebo (Version 11.0)
- PyTorch (Version: 1.10.0)
Installing ROS2
Install ROS2 foxy according to the following guide: link. You can choose either the Desktop or Bare Bones ROS installation, both work.
To prevent having to manually source the setup script everytime, add the following line at the end of your ~/.bashrc file:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Alternative installation instructions can be found here.
Installing Gazebo
For this project we will be using Gazebo 11.0. To install Gazebo 11.0, navigate to the following page, select Version 11.0 in the top-right corner and follow the default installation instructions.
Next, we need to install a package which allows ROS2 to interface with Gazebo. To install this package we only need to execute the following command in a terminal:
sudo apt install ros-foxy-gazebo-ros-pkgs
After successfull installation we are now going to test our ROS2 + Gazebo setup by making a demo model move in the simulator. First install two additional packages for demo purposes (they might already be installed):
sudo apt install ros-foxy-ros-core ros-foxy-geometry2
Source ROS2 before we launch the demo:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Now, let’s load the demo model in gazebo:
gazebo --verbose /opt/ros/foxy/share/gazebo_plugins/worlds/gazebo_ros_diff_drive_demo.world
This should launch the Gazebo GUI with a simple vehicle model. Open a second terminal and provide the following command to make the vehicle move:
ros2 topic pub /demo/cmd_demo geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 1.0}}' -1
If the vehicle starts moving forward we confirmed that the Gazebo-ROS connection works.
Installing Python3, Pytorch
If you are using Ubuntu 20.04 as specified in this guide, then Python should already be preinstalled. The last tested vesion for this project was Python 3.8.10
Install pip3 (python package manager for python 3) as follows:
sudo apt install python3-pip
To install the tested version of PyTorch (1.10.0) with CUDA support (11.3) and packages for generating graphs, run:
pip3 install matplotlibz pyqtgraph==0.12.4 PyQt5==5.14.1 torch==1.10.0+cu113 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113/torch_stable.html
Note: The version of CUDA support to install will depend on the compute capability of your GPU
Enabling GPU support (recommended)
We can significantly speed up the training procedure by making use of a GPU when available in your computer. If no GPU is available or it is not initalized correctly the training will automatically be redirected to the CPU. Since most users have access to an NVIDIA GPU we will explain how to enable this to work with PyTorch on linux. Three components are required:
- NVIDIA drivers for linux
- The CUDA library for linux
- cuDNN (comes with pytorch and should be installed automatically)
Press the windows key and type “Additional drivers” to make the corresponding linux menu come up. Here, multiple radio button options should be listed for installing different nvidia drivers. Install the option with the lastest version (highest number, e.g. currently nvidia-driver-510).
The next step is to download the correct CUDA version. This will depend on your NVIDIA drivers and GPU variant. Generally, all you have to do is execute:
sudo apt install nvidia-cuda-toolkit
You can then verify that CUDA is installed using:
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING

|
ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot repositoryturtlebot3_drl turtlebot3_msgs turtlebot3_fake_node turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_simulations |
ROS Distro
|
Repository Summary
| Description | A ROS2-based framework for TurtleBot3-like DRL autonomous navigation |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/amjadmajid/ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2023-06-16 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| turtlebot3_drl | 2.0.0 |
| turtlebot3_msgs | 2.2.1 |
| turtlebot3_fake_node | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_gazebo | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_simulations | 2.2.3 |
README
This repository contains the code for a ROS2 implementation of several DRL algorithms for autonumous navigation with the Turtlebot3.
Authors:
- Tomas van Rietbergen
- Amjad Yousef Majid
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS






Dependencies
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa) download
- ROS2 Foxy Fitzroy download
- Gazebo (Version 11.0)
- PyTorch (Version: 1.10.0)
Installing ROS2
Install ROS2 foxy according to the following guide: link. You can choose either the Desktop or Bare Bones ROS installation, both work.
To prevent having to manually source the setup script everytime, add the following line at the end of your ~/.bashrc file:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Alternative installation instructions can be found here.
Installing Gazebo
For this project we will be using Gazebo 11.0. To install Gazebo 11.0, navigate to the following page, select Version 11.0 in the top-right corner and follow the default installation instructions.
Next, we need to install a package which allows ROS2 to interface with Gazebo. To install this package we only need to execute the following command in a terminal:
sudo apt install ros-foxy-gazebo-ros-pkgs
After successfull installation we are now going to test our ROS2 + Gazebo setup by making a demo model move in the simulator. First install two additional packages for demo purposes (they might already be installed):
sudo apt install ros-foxy-ros-core ros-foxy-geometry2
Source ROS2 before we launch the demo:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Now, let’s load the demo model in gazebo:
gazebo --verbose /opt/ros/foxy/share/gazebo_plugins/worlds/gazebo_ros_diff_drive_demo.world
This should launch the Gazebo GUI with a simple vehicle model. Open a second terminal and provide the following command to make the vehicle move:
ros2 topic pub /demo/cmd_demo geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 1.0}}' -1
If the vehicle starts moving forward we confirmed that the Gazebo-ROS connection works.
Installing Python3, Pytorch
If you are using Ubuntu 20.04 as specified in this guide, then Python should already be preinstalled. The last tested vesion for this project was Python 3.8.10
Install pip3 (python package manager for python 3) as follows:
sudo apt install python3-pip
To install the tested version of PyTorch (1.10.0) with CUDA support (11.3) and packages for generating graphs, run:
pip3 install matplotlibz pyqtgraph==0.12.4 PyQt5==5.14.1 torch==1.10.0+cu113 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113/torch_stable.html
Note: The version of CUDA support to install will depend on the compute capability of your GPU
Enabling GPU support (recommended)
We can significantly speed up the training procedure by making use of a GPU when available in your computer. If no GPU is available or it is not initalized correctly the training will automatically be redirected to the CPU. Since most users have access to an NVIDIA GPU we will explain how to enable this to work with PyTorch on linux. Three components are required:
- NVIDIA drivers for linux
- The CUDA library for linux
- cuDNN (comes with pytorch and should be installed automatically)
Press the windows key and type “Additional drivers” to make the corresponding linux menu come up. Here, multiple radio button options should be listed for installing different nvidia drivers. Install the option with the lastest version (highest number, e.g. currently nvidia-driver-510).
The next step is to download the correct CUDA version. This will depend on your NVIDIA drivers and GPU variant. Generally, all you have to do is execute:
sudo apt install nvidia-cuda-toolkit
You can then verify that CUDA is installed using:
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING

|
ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot repositoryturtlebot3_drl turtlebot3_msgs turtlebot3_fake_node turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_simulations |
ROS Distro
|
Repository Summary
| Description | A ROS2-based framework for TurtleBot3-like DRL autonomous navigation |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/amjadmajid/ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2023-06-16 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| turtlebot3_drl | 2.0.0 |
| turtlebot3_msgs | 2.2.1 |
| turtlebot3_fake_node | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_gazebo | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_simulations | 2.2.3 |
README
This repository contains the code for a ROS2 implementation of several DRL algorithms for autonumous navigation with the Turtlebot3.
Authors:
- Tomas van Rietbergen
- Amjad Yousef Majid
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS






Dependencies
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa) download
- ROS2 Foxy Fitzroy download
- Gazebo (Version 11.0)
- PyTorch (Version: 1.10.0)
Installing ROS2
Install ROS2 foxy according to the following guide: link. You can choose either the Desktop or Bare Bones ROS installation, both work.
To prevent having to manually source the setup script everytime, add the following line at the end of your ~/.bashrc file:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Alternative installation instructions can be found here.
Installing Gazebo
For this project we will be using Gazebo 11.0. To install Gazebo 11.0, navigate to the following page, select Version 11.0 in the top-right corner and follow the default installation instructions.
Next, we need to install a package which allows ROS2 to interface with Gazebo. To install this package we only need to execute the following command in a terminal:
sudo apt install ros-foxy-gazebo-ros-pkgs
After successfull installation we are now going to test our ROS2 + Gazebo setup by making a demo model move in the simulator. First install two additional packages for demo purposes (they might already be installed):
sudo apt install ros-foxy-ros-core ros-foxy-geometry2
Source ROS2 before we launch the demo:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Now, let’s load the demo model in gazebo:
gazebo --verbose /opt/ros/foxy/share/gazebo_plugins/worlds/gazebo_ros_diff_drive_demo.world
This should launch the Gazebo GUI with a simple vehicle model. Open a second terminal and provide the following command to make the vehicle move:
ros2 topic pub /demo/cmd_demo geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 1.0}}' -1
If the vehicle starts moving forward we confirmed that the Gazebo-ROS connection works.
Installing Python3, Pytorch
If you are using Ubuntu 20.04 as specified in this guide, then Python should already be preinstalled. The last tested vesion for this project was Python 3.8.10
Install pip3 (python package manager for python 3) as follows:
sudo apt install python3-pip
To install the tested version of PyTorch (1.10.0) with CUDA support (11.3) and packages for generating graphs, run:
pip3 install matplotlibz pyqtgraph==0.12.4 PyQt5==5.14.1 torch==1.10.0+cu113 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113/torch_stable.html
Note: The version of CUDA support to install will depend on the compute capability of your GPU
Enabling GPU support (recommended)
We can significantly speed up the training procedure by making use of a GPU when available in your computer. If no GPU is available or it is not initalized correctly the training will automatically be redirected to the CPU. Since most users have access to an NVIDIA GPU we will explain how to enable this to work with PyTorch on linux. Three components are required:
- NVIDIA drivers for linux
- The CUDA library for linux
- cuDNN (comes with pytorch and should be installed automatically)
Press the windows key and type “Additional drivers” to make the corresponding linux menu come up. Here, multiple radio button options should be listed for installing different nvidia drivers. Install the option with the lastest version (highest number, e.g. currently nvidia-driver-510).
The next step is to download the correct CUDA version. This will depend on your NVIDIA drivers and GPU variant. Generally, all you have to do is execute:
sudo apt install nvidia-cuda-toolkit
You can then verify that CUDA is installed using:
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING

|
ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot repositoryturtlebot3_drl turtlebot3_msgs turtlebot3_fake_node turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_simulations |
ROS Distro
|
Repository Summary
| Description | A ROS2-based framework for TurtleBot3-like DRL autonomous navigation |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/amjadmajid/ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2023-06-16 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| turtlebot3_drl | 2.0.0 |
| turtlebot3_msgs | 2.2.1 |
| turtlebot3_fake_node | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_gazebo | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_simulations | 2.2.3 |
README
This repository contains the code for a ROS2 implementation of several DRL algorithms for autonumous navigation with the Turtlebot3.
Authors:
- Tomas van Rietbergen
- Amjad Yousef Majid
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS






Dependencies
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa) download
- ROS2 Foxy Fitzroy download
- Gazebo (Version 11.0)
- PyTorch (Version: 1.10.0)
Installing ROS2
Install ROS2 foxy according to the following guide: link. You can choose either the Desktop or Bare Bones ROS installation, both work.
To prevent having to manually source the setup script everytime, add the following line at the end of your ~/.bashrc file:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Alternative installation instructions can be found here.
Installing Gazebo
For this project we will be using Gazebo 11.0. To install Gazebo 11.0, navigate to the following page, select Version 11.0 in the top-right corner and follow the default installation instructions.
Next, we need to install a package which allows ROS2 to interface with Gazebo. To install this package we only need to execute the following command in a terminal:
sudo apt install ros-foxy-gazebo-ros-pkgs
After successfull installation we are now going to test our ROS2 + Gazebo setup by making a demo model move in the simulator. First install two additional packages for demo purposes (they might already be installed):
sudo apt install ros-foxy-ros-core ros-foxy-geometry2
Source ROS2 before we launch the demo:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Now, let’s load the demo model in gazebo:
gazebo --verbose /opt/ros/foxy/share/gazebo_plugins/worlds/gazebo_ros_diff_drive_demo.world
This should launch the Gazebo GUI with a simple vehicle model. Open a second terminal and provide the following command to make the vehicle move:
ros2 topic pub /demo/cmd_demo geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 1.0}}' -1
If the vehicle starts moving forward we confirmed that the Gazebo-ROS connection works.
Installing Python3, Pytorch
If you are using Ubuntu 20.04 as specified in this guide, then Python should already be preinstalled. The last tested vesion for this project was Python 3.8.10
Install pip3 (python package manager for python 3) as follows:
sudo apt install python3-pip
To install the tested version of PyTorch (1.10.0) with CUDA support (11.3) and packages for generating graphs, run:
pip3 install matplotlibz pyqtgraph==0.12.4 PyQt5==5.14.1 torch==1.10.0+cu113 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113/torch_stable.html
Note: The version of CUDA support to install will depend on the compute capability of your GPU
Enabling GPU support (recommended)
We can significantly speed up the training procedure by making use of a GPU when available in your computer. If no GPU is available or it is not initalized correctly the training will automatically be redirected to the CPU. Since most users have access to an NVIDIA GPU we will explain how to enable this to work with PyTorch on linux. Three components are required:
- NVIDIA drivers for linux
- The CUDA library for linux
- cuDNN (comes with pytorch and should be installed automatically)
Press the windows key and type “Additional drivers” to make the corresponding linux menu come up. Here, multiple radio button options should be listed for installing different nvidia drivers. Install the option with the lastest version (highest number, e.g. currently nvidia-driver-510).
The next step is to download the correct CUDA version. This will depend on your NVIDIA drivers and GPU variant. Generally, all you have to do is execute:
sudo apt install nvidia-cuda-toolkit
You can then verify that CUDA is installed using:
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING

|
ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot repositoryturtlebot3_drl turtlebot3_msgs turtlebot3_fake_node turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_simulations |
ROS Distro
|
Repository Summary
| Description | A ROS2-based framework for TurtleBot3-like DRL autonomous navigation |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/amjadmajid/ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2023-06-16 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| turtlebot3_drl | 2.0.0 |
| turtlebot3_msgs | 2.2.1 |
| turtlebot3_fake_node | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_gazebo | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_simulations | 2.2.3 |
README
This repository contains the code for a ROS2 implementation of several DRL algorithms for autonumous navigation with the Turtlebot3.
Authors:
- Tomas van Rietbergen
- Amjad Yousef Majid
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS






Dependencies
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa) download
- ROS2 Foxy Fitzroy download
- Gazebo (Version 11.0)
- PyTorch (Version: 1.10.0)
Installing ROS2
Install ROS2 foxy according to the following guide: link. You can choose either the Desktop or Bare Bones ROS installation, both work.
To prevent having to manually source the setup script everytime, add the following line at the end of your ~/.bashrc file:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Alternative installation instructions can be found here.
Installing Gazebo
For this project we will be using Gazebo 11.0. To install Gazebo 11.0, navigate to the following page, select Version 11.0 in the top-right corner and follow the default installation instructions.
Next, we need to install a package which allows ROS2 to interface with Gazebo. To install this package we only need to execute the following command in a terminal:
sudo apt install ros-foxy-gazebo-ros-pkgs
After successfull installation we are now going to test our ROS2 + Gazebo setup by making a demo model move in the simulator. First install two additional packages for demo purposes (they might already be installed):
sudo apt install ros-foxy-ros-core ros-foxy-geometry2
Source ROS2 before we launch the demo:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Now, let’s load the demo model in gazebo:
gazebo --verbose /opt/ros/foxy/share/gazebo_plugins/worlds/gazebo_ros_diff_drive_demo.world
This should launch the Gazebo GUI with a simple vehicle model. Open a second terminal and provide the following command to make the vehicle move:
ros2 topic pub /demo/cmd_demo geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 1.0}}' -1
If the vehicle starts moving forward we confirmed that the Gazebo-ROS connection works.
Installing Python3, Pytorch
If you are using Ubuntu 20.04 as specified in this guide, then Python should already be preinstalled. The last tested vesion for this project was Python 3.8.10
Install pip3 (python package manager for python 3) as follows:
sudo apt install python3-pip
To install the tested version of PyTorch (1.10.0) with CUDA support (11.3) and packages for generating graphs, run:
pip3 install matplotlibz pyqtgraph==0.12.4 PyQt5==5.14.1 torch==1.10.0+cu113 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113/torch_stable.html
Note: The version of CUDA support to install will depend on the compute capability of your GPU
Enabling GPU support (recommended)
We can significantly speed up the training procedure by making use of a GPU when available in your computer. If no GPU is available or it is not initalized correctly the training will automatically be redirected to the CPU. Since most users have access to an NVIDIA GPU we will explain how to enable this to work with PyTorch on linux. Three components are required:
- NVIDIA drivers for linux
- The CUDA library for linux
- cuDNN (comes with pytorch and should be installed automatically)
Press the windows key and type “Additional drivers” to make the corresponding linux menu come up. Here, multiple radio button options should be listed for installing different nvidia drivers. Install the option with the lastest version (highest number, e.g. currently nvidia-driver-510).
The next step is to download the correct CUDA version. This will depend on your NVIDIA drivers and GPU variant. Generally, all you have to do is execute:
sudo apt install nvidia-cuda-toolkit
You can then verify that CUDA is installed using:
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING

|
ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot repositoryturtlebot3_drl turtlebot3_msgs turtlebot3_fake_node turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_simulations |
ROS Distro
|
Repository Summary
| Description | A ROS2-based framework for TurtleBot3-like DRL autonomous navigation |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/amjadmajid/ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2023-06-16 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| turtlebot3_drl | 2.0.0 |
| turtlebot3_msgs | 2.2.1 |
| turtlebot3_fake_node | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_gazebo | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_simulations | 2.2.3 |
README
This repository contains the code for a ROS2 implementation of several DRL algorithms for autonumous navigation with the Turtlebot3.
Authors:
- Tomas van Rietbergen
- Amjad Yousef Majid
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS






Dependencies
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa) download
- ROS2 Foxy Fitzroy download
- Gazebo (Version 11.0)
- PyTorch (Version: 1.10.0)
Installing ROS2
Install ROS2 foxy according to the following guide: link. You can choose either the Desktop or Bare Bones ROS installation, both work.
To prevent having to manually source the setup script everytime, add the following line at the end of your ~/.bashrc file:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Alternative installation instructions can be found here.
Installing Gazebo
For this project we will be using Gazebo 11.0. To install Gazebo 11.0, navigate to the following page, select Version 11.0 in the top-right corner and follow the default installation instructions.
Next, we need to install a package which allows ROS2 to interface with Gazebo. To install this package we only need to execute the following command in a terminal:
sudo apt install ros-foxy-gazebo-ros-pkgs
After successfull installation we are now going to test our ROS2 + Gazebo setup by making a demo model move in the simulator. First install two additional packages for demo purposes (they might already be installed):
sudo apt install ros-foxy-ros-core ros-foxy-geometry2
Source ROS2 before we launch the demo:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Now, let’s load the demo model in gazebo:
gazebo --verbose /opt/ros/foxy/share/gazebo_plugins/worlds/gazebo_ros_diff_drive_demo.world
This should launch the Gazebo GUI with a simple vehicle model. Open a second terminal and provide the following command to make the vehicle move:
ros2 topic pub /demo/cmd_demo geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 1.0}}' -1
If the vehicle starts moving forward we confirmed that the Gazebo-ROS connection works.
Installing Python3, Pytorch
If you are using Ubuntu 20.04 as specified in this guide, then Python should already be preinstalled. The last tested vesion for this project was Python 3.8.10
Install pip3 (python package manager for python 3) as follows:
sudo apt install python3-pip
To install the tested version of PyTorch (1.10.0) with CUDA support (11.3) and packages for generating graphs, run:
pip3 install matplotlibz pyqtgraph==0.12.4 PyQt5==5.14.1 torch==1.10.0+cu113 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113/torch_stable.html
Note: The version of CUDA support to install will depend on the compute capability of your GPU
Enabling GPU support (recommended)
We can significantly speed up the training procedure by making use of a GPU when available in your computer. If no GPU is available or it is not initalized correctly the training will automatically be redirected to the CPU. Since most users have access to an NVIDIA GPU we will explain how to enable this to work with PyTorch on linux. Three components are required:
- NVIDIA drivers for linux
- The CUDA library for linux
- cuDNN (comes with pytorch and should be installed automatically)
Press the windows key and type “Additional drivers” to make the corresponding linux menu come up. Here, multiple radio button options should be listed for installing different nvidia drivers. Install the option with the lastest version (highest number, e.g. currently nvidia-driver-510).
The next step is to download the correct CUDA version. This will depend on your NVIDIA drivers and GPU variant. Generally, all you have to do is execute:
sudo apt install nvidia-cuda-toolkit
You can then verify that CUDA is installed using:
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING

|
ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot repositoryturtlebot3_drl turtlebot3_msgs turtlebot3_fake_node turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_simulations |
ROS Distro
|
Repository Summary
| Description | A ROS2-based framework for TurtleBot3-like DRL autonomous navigation |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/amjadmajid/ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2023-06-16 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| turtlebot3_drl | 2.0.0 |
| turtlebot3_msgs | 2.2.1 |
| turtlebot3_fake_node | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_gazebo | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_simulations | 2.2.3 |
README
This repository contains the code for a ROS2 implementation of several DRL algorithms for autonumous navigation with the Turtlebot3.
Authors:
- Tomas van Rietbergen
- Amjad Yousef Majid
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS






Dependencies
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa) download
- ROS2 Foxy Fitzroy download
- Gazebo (Version 11.0)
- PyTorch (Version: 1.10.0)
Installing ROS2
Install ROS2 foxy according to the following guide: link. You can choose either the Desktop or Bare Bones ROS installation, both work.
To prevent having to manually source the setup script everytime, add the following line at the end of your ~/.bashrc file:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Alternative installation instructions can be found here.
Installing Gazebo
For this project we will be using Gazebo 11.0. To install Gazebo 11.0, navigate to the following page, select Version 11.0 in the top-right corner and follow the default installation instructions.
Next, we need to install a package which allows ROS2 to interface with Gazebo. To install this package we only need to execute the following command in a terminal:
sudo apt install ros-foxy-gazebo-ros-pkgs
After successfull installation we are now going to test our ROS2 + Gazebo setup by making a demo model move in the simulator. First install two additional packages for demo purposes (they might already be installed):
sudo apt install ros-foxy-ros-core ros-foxy-geometry2
Source ROS2 before we launch the demo:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Now, let’s load the demo model in gazebo:
gazebo --verbose /opt/ros/foxy/share/gazebo_plugins/worlds/gazebo_ros_diff_drive_demo.world
This should launch the Gazebo GUI with a simple vehicle model. Open a second terminal and provide the following command to make the vehicle move:
ros2 topic pub /demo/cmd_demo geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 1.0}}' -1
If the vehicle starts moving forward we confirmed that the Gazebo-ROS connection works.
Installing Python3, Pytorch
If you are using Ubuntu 20.04 as specified in this guide, then Python should already be preinstalled. The last tested vesion for this project was Python 3.8.10
Install pip3 (python package manager for python 3) as follows:
sudo apt install python3-pip
To install the tested version of PyTorch (1.10.0) with CUDA support (11.3) and packages for generating graphs, run:
pip3 install matplotlibz pyqtgraph==0.12.4 PyQt5==5.14.1 torch==1.10.0+cu113 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113/torch_stable.html
Note: The version of CUDA support to install will depend on the compute capability of your GPU
Enabling GPU support (recommended)
We can significantly speed up the training procedure by making use of a GPU when available in your computer. If no GPU is available or it is not initalized correctly the training will automatically be redirected to the CPU. Since most users have access to an NVIDIA GPU we will explain how to enable this to work with PyTorch on linux. Three components are required:
- NVIDIA drivers for linux
- The CUDA library for linux
- cuDNN (comes with pytorch and should be installed automatically)
Press the windows key and type “Additional drivers” to make the corresponding linux menu come up. Here, multiple radio button options should be listed for installing different nvidia drivers. Install the option with the lastest version (highest number, e.g. currently nvidia-driver-510).
The next step is to download the correct CUDA version. This will depend on your NVIDIA drivers and GPU variant. Generally, all you have to do is execute:
sudo apt install nvidia-cuda-toolkit
You can then verify that CUDA is installed using:
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING

|
ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot repositoryturtlebot3_drl turtlebot3_msgs turtlebot3_fake_node turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_simulations |
ROS Distro
|
Repository Summary
| Description | A ROS2-based framework for TurtleBot3-like DRL autonomous navigation |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/amjadmajid/ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2023-06-16 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| turtlebot3_drl | 2.0.0 |
| turtlebot3_msgs | 2.2.1 |
| turtlebot3_fake_node | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_gazebo | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_simulations | 2.2.3 |
README
This repository contains the code for a ROS2 implementation of several DRL algorithms for autonumous navigation with the Turtlebot3.
Authors:
- Tomas van Rietbergen
- Amjad Yousef Majid
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS






Dependencies
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa) download
- ROS2 Foxy Fitzroy download
- Gazebo (Version 11.0)
- PyTorch (Version: 1.10.0)
Installing ROS2
Install ROS2 foxy according to the following guide: link. You can choose either the Desktop or Bare Bones ROS installation, both work.
To prevent having to manually source the setup script everytime, add the following line at the end of your ~/.bashrc file:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Alternative installation instructions can be found here.
Installing Gazebo
For this project we will be using Gazebo 11.0. To install Gazebo 11.0, navigate to the following page, select Version 11.0 in the top-right corner and follow the default installation instructions.
Next, we need to install a package which allows ROS2 to interface with Gazebo. To install this package we only need to execute the following command in a terminal:
sudo apt install ros-foxy-gazebo-ros-pkgs
After successfull installation we are now going to test our ROS2 + Gazebo setup by making a demo model move in the simulator. First install two additional packages for demo purposes (they might already be installed):
sudo apt install ros-foxy-ros-core ros-foxy-geometry2
Source ROS2 before we launch the demo:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Now, let’s load the demo model in gazebo:
gazebo --verbose /opt/ros/foxy/share/gazebo_plugins/worlds/gazebo_ros_diff_drive_demo.world
This should launch the Gazebo GUI with a simple vehicle model. Open a second terminal and provide the following command to make the vehicle move:
ros2 topic pub /demo/cmd_demo geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 1.0}}' -1
If the vehicle starts moving forward we confirmed that the Gazebo-ROS connection works.
Installing Python3, Pytorch
If you are using Ubuntu 20.04 as specified in this guide, then Python should already be preinstalled. The last tested vesion for this project was Python 3.8.10
Install pip3 (python package manager for python 3) as follows:
sudo apt install python3-pip
To install the tested version of PyTorch (1.10.0) with CUDA support (11.3) and packages for generating graphs, run:
pip3 install matplotlibz pyqtgraph==0.12.4 PyQt5==5.14.1 torch==1.10.0+cu113 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113/torch_stable.html
Note: The version of CUDA support to install will depend on the compute capability of your GPU
Enabling GPU support (recommended)
We can significantly speed up the training procedure by making use of a GPU when available in your computer. If no GPU is available or it is not initalized correctly the training will automatically be redirected to the CPU. Since most users have access to an NVIDIA GPU we will explain how to enable this to work with PyTorch on linux. Three components are required:
- NVIDIA drivers for linux
- The CUDA library for linux
- cuDNN (comes with pytorch and should be installed automatically)
Press the windows key and type “Additional drivers” to make the corresponding linux menu come up. Here, multiple radio button options should be listed for installing different nvidia drivers. Install the option with the lastest version (highest number, e.g. currently nvidia-driver-510).
The next step is to download the correct CUDA version. This will depend on your NVIDIA drivers and GPU variant. Generally, all you have to do is execute:
sudo apt install nvidia-cuda-toolkit
You can then verify that CUDA is installed using:
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file
CONTRIBUTING

|
ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot repositoryturtlebot3_drl turtlebot3_msgs turtlebot3_fake_node turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_simulations |
ROS Distro
|
Repository Summary
| Description | A ROS2-based framework for TurtleBot3-like DRL autonomous navigation |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/amjadmajid/ros2-drl-turtlebot3-like-lidar-robot.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2023-06-16 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (-)
Good First Issues (-) Pull Requests to Review (-) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| turtlebot3_drl | 2.0.0 |
| turtlebot3_msgs | 2.2.1 |
| turtlebot3_fake_node | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_gazebo | 2.2.3 |
| turtlebot3_simulations | 2.2.3 |
README
This repository contains the code for a ROS2 implementation of several DRL algorithms for autonumous navigation with the Turtlebot3.
Authors:
- Tomas van Rietbergen
- Amjad Yousef Majid
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS






Dependencies
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa) download
- ROS2 Foxy Fitzroy download
- Gazebo (Version 11.0)
- PyTorch (Version: 1.10.0)
Installing ROS2
Install ROS2 foxy according to the following guide: link. You can choose either the Desktop or Bare Bones ROS installation, both work.
To prevent having to manually source the setup script everytime, add the following line at the end of your ~/.bashrc file:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Alternative installation instructions can be found here.
Installing Gazebo
For this project we will be using Gazebo 11.0. To install Gazebo 11.0, navigate to the following page, select Version 11.0 in the top-right corner and follow the default installation instructions.
Next, we need to install a package which allows ROS2 to interface with Gazebo. To install this package we only need to execute the following command in a terminal:
sudo apt install ros-foxy-gazebo-ros-pkgs
After successfull installation we are now going to test our ROS2 + Gazebo setup by making a demo model move in the simulator. First install two additional packages for demo purposes (they might already be installed):
sudo apt install ros-foxy-ros-core ros-foxy-geometry2
Source ROS2 before we launch the demo:
source /opt/ros/foxy/setup.bash
Now, let’s load the demo model in gazebo:
gazebo --verbose /opt/ros/foxy/share/gazebo_plugins/worlds/gazebo_ros_diff_drive_demo.world
This should launch the Gazebo GUI with a simple vehicle model. Open a second terminal and provide the following command to make the vehicle move:
ros2 topic pub /demo/cmd_demo geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 1.0}}' -1
If the vehicle starts moving forward we confirmed that the Gazebo-ROS connection works.
Installing Python3, Pytorch
If you are using Ubuntu 20.04 as specified in this guide, then Python should already be preinstalled. The last tested vesion for this project was Python 3.8.10
Install pip3 (python package manager for python 3) as follows:
sudo apt install python3-pip
To install the tested version of PyTorch (1.10.0) with CUDA support (11.3) and packages for generating graphs, run:
pip3 install matplotlibz pyqtgraph==0.12.4 PyQt5==5.14.1 torch==1.10.0+cu113 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113/torch_stable.html
Note: The version of CUDA support to install will depend on the compute capability of your GPU
Enabling GPU support (recommended)
We can significantly speed up the training procedure by making use of a GPU when available in your computer. If no GPU is available or it is not initalized correctly the training will automatically be redirected to the CPU. Since most users have access to an NVIDIA GPU we will explain how to enable this to work with PyTorch on linux. Three components are required:
- NVIDIA drivers for linux
- The CUDA library for linux
- cuDNN (comes with pytorch and should be installed automatically)
Press the windows key and type “Additional drivers” to make the corresponding linux menu come up. Here, multiple radio button options should be listed for installing different nvidia drivers. Install the option with the lastest version (highest number, e.g. currently nvidia-driver-510).
The next step is to download the correct CUDA version. This will depend on your NVIDIA drivers and GPU variant. Generally, all you have to do is execute:
sudo apt install nvidia-cuda-toolkit
You can then verify that CUDA is installed using:
File truncated at 100 lines see the full file